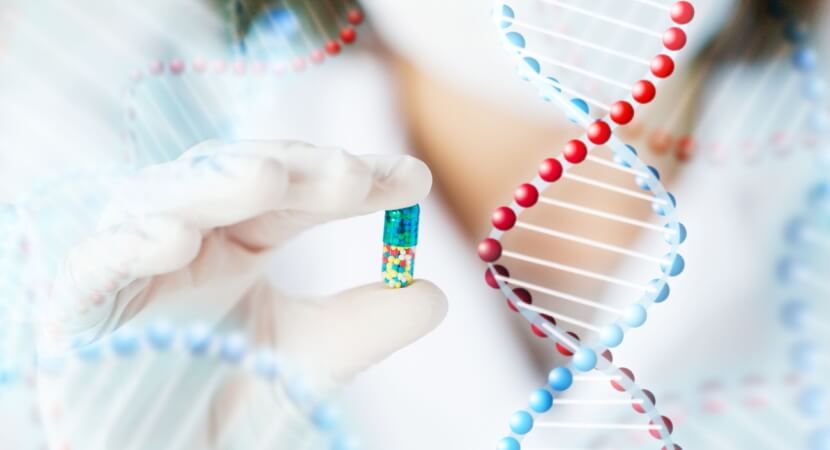
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Today's third-generation IVF has been developed to check the embryos genetically before transfering back to the uterus. The technology not only increases the healthy take-home baby rate, but also reduces the chance of miscarriage due to genetic defects.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is a technology to detect the chromosomal abnormalities in embryonic cells. According to the purpose of the test, it can be subdivided into PGT-A or PGT-M/-SR:
PGT-A, formerly known as PGS
Using the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) to check whether there is additional or insufficient copy number of chromosomes in embryonic cells.
PGT-M/-SR, formerly known as PGD
With PGT-M and PGT-SR, embryos without monogenic disorder or abnormalities in structural chromosomal rearrangements (such as translocations or inversions) can be selected for embryo transfer.
Who are suitable for PGT?
The following 6 types of patients may benefit from PGT:
- Advanced maternal age (35 years old or above)
- Women experienced recurrent miscarriage (2 or more consecutive miscarriages)
- Women experienced recurrent implantation / fertilization failure
- Previous pregnancy with chromosomal abnormalities
- With family history of chromosomal abnormalities
- With family history of congenital genetic disorder
- Severe male infertility problem







 Egg Freezing
Egg Freezing Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM)for Fertility
Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM)for Fertility